Mastering Habit Formation for Lifelong Learning and Success
Written on
Chapter 1: The Importance of Habit Formation
In the rapidly evolving job market, acquiring new skills is crucial for future success. The World Economic Forum reports that over half of the workforce will require retraining within the next few years. With technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence, the landscape of work is shifting dramatically. McKinsey estimates that around 45% of jobs could be automated using existing technology, freeing individuals to leverage essential soft skills like creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
To thrive in this changing environment, it's vital to cultivate a mindset geared towards habit formation. The skills we rely on today may differ significantly from those required just a year ago. Factors such as globalization and demographic shifts also contribute to evolving workplace demands. To stay competitive, we must embrace lifelong learning, regularly updating our knowledge and abilities.
To foster continuous learning, dedicate a specific time each day to develop a learning habit. Establishing habits automates behaviors, increasing the likelihood of consistent engagement in these activities. How often have you resolved to exercise more or sleep earlier only to fall short? Until these actions become habitual, adopting new behaviors can be a challenge. The silver lining is that our lives are filled with habits—both beneficial and detrimental. Our brains favor habits as they conserve energy, allowing for lower mental exertion.
We will delve into the process of forming habits through three key stages.

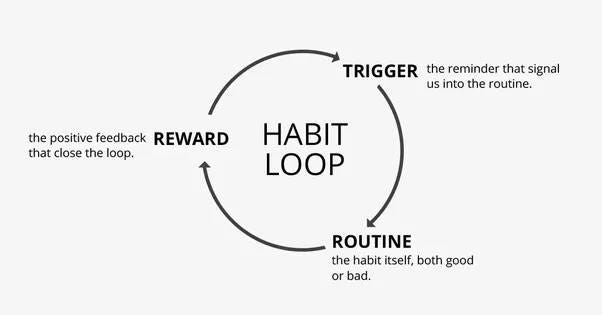
Step 1: Understand the Habit Loop
The first step to establishing a new habit is to comprehend the habit loop, which consists of three components: trigger, routine, and reward. It begins with a cue that prompts a craving for a reward, encouraging your brain to engage in a specific behavior. As you cultivate a habit, remember to reward yourself—whether it's a piece of chocolate or a brief chat with a colleague. These positive reinforcements help your brain associate pleasure with the behavior, solidifying the habit over time.
The first video, THE 20 SECOND RULE - HOW TO BUILD A NEW HABIT, discusses strategies for forming habits effectively. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing the effort required to initiate a new behavior.
Step 2: Link to Existing Habits
Another effective strategy for embedding a new learning habit is to connect it with an established behavior. For instance, if you enjoy coffee in the morning while browsing social media, consider dedicating ten minutes to learning instead. This could involve reading an interesting article unrelated to work. Starting with topics that captivate you can significantly enhance your engagement and make learning more enjoyable, ultimately reinforcing your habit.
To illustrate, pairing your morning coffee with a learning activity can leverage the strength of your coffee ritual to foster a new habit.
Step 3: Implement a Habit Tracker
For those who thrive on goal-setting, tracking your progress can be an impactful motivator. Taking charge of your self-management can yield rewards that surpass simple treats like chocolate or coffee.
Habit Loop Components
The habit loop consists of the following elements:
- Trigger (Cue): This initiates your habit and can be influenced by location, time of day, emotional state, or previous habits. For example, the smell of coffee may trigger a desire for a cup.
- Routine: This is the behavior you wish to change or reinforce, such as opting for stairs instead of elevators.
- Reward: This aspect reinforces the behavior, making it more likely to be repeated. Rewards can range from tangible items like chocolate to intangible ones like a favorite TV show.
Creating a habit using the habit loop involves practicing the new behavior consistently over a period—typically around eight weeks—until it becomes automatic.
Hacking Bad Habits
Recognizing the power of the habit loop can help in overcoming detrimental habits. Charles Duhigg, author of The Power of Habit, provides a framework for transforming negative behaviors:
- Identify the Routine: Recognize the habit you want to change. For instance, if you frequently buy hot chocolate in the afternoon, note this behavior.
- Experiment with Rewards: Rewards may not always be apparent. For instance, the reward for your hot chocolate habit might stem from social interaction rather than the drink itself.
- Pinpoint Triggers: Analyze the circumstances that lead to your habit. Consider factors like location, time, emotional state, and who is around you.
- Develop a Plan: Once you identify triggers, create a strategy to replace the undesirable habit with a healthier alternative.
The second video, How to Build Good Habits: Atomic Habits by James Clear, provides insights into habit formation and strategies for success. It emphasizes the significance of incremental changes and consistency.
Make Learning Part of Your Daily Routine
Set specific learning goals for a defined timeframe, whether it be three months, six months, or a year. Consider these guiding questions to facilitate your learning process:
- What knowledge can I gain from this experience?
- How can I enhance my learning?
- How can I apply what I learn?
After establishing your learning goals, return to the habit loop. The core component—routine—may involve studying for an exam, but triggers and rewards are essential for completing the loop.
Effective triggers can include specific locations or times for studying, while rewards should provide immediate gratification to reinforce your commitment.
Utilizing the Token Economy
The token economy approach involves using tokens that can be exchanged for rewards, enhancing motivation. For instance, students might receive tokens for completing tasks, which they can later trade for prizes. This concept can be applied to personal goals, such as exercising regularly or studying effectively.
By choosing a rewarding token and integrating it into your routine, you can develop lasting habits that contribute to your success. As you navigate the complexities of learning and personal growth, remember that with the right strategies and incentives, you can create a fulfilling and productive habit.