The Fascinating Science Behind the Aurorae Phenomenon
Written on
Chapter 1: The Enigma of Aurorae
Have you ever pondered the origins of the breathtaking aurorae we observe on Earth?

Image credit: Painting by Shahla
In the image above, you can see my interpretation of an aurora scene, created during my exploration of how to depict the northern lights. This artistic endeavor also sparked my curiosity regarding the scientific phenomena that produce these mesmerizing displays. If you're intrigued as well, let’s delve into the processes behind these extraordinary sights.
The northern lights, also referred to as the aurora borealis in the northern hemisphere and the aurora australis in the south, have captivated and inspired humanity for centuries. Their origins, however, remain a subject of scientific inquiry.
The awe-inspiring lights visible in the night sky during auroras are primarily a result of solar activity. The Sun, which illuminates our world during the day, is also the source of these spectacular displays. Solar storms release vast clouds of electrically charged particles that can traverse millions of kilometers, and some of these particles ultimately reach our planet.
Earth itself functions as a massive magnet, possessing a magnetic field comprised of closed lines that encircle the planet and extend through its poles. When charged particles from solar storms are deflected or trapped by this magnetic field, they are accelerated along its lines, eventually colliding with atmospheric particles near the poles.
As a result, the patterns we observe in auroras mirror the magnetic field lines of Earth. The illumination we witness arises from these high-energy particles colliding with air particles. When these atmospheric particles interact with energetic cosmic particles, they absorb energy, become excited, and subsequently release that energy in the form of light as they return to their normal state.
The emitted light varies in color based on the wavelength and the specific elements involved. The primary gases in Earth’s atmosphere, nitrogen and oxygen, give rise to the predominant colors we see during auroras. Nitrogen atoms emit hues of purple and pink, while nitrogen ions produce blue waves. The height at which these interactions occur also influences the colors observed:
- The yellowish-green shades, predominantly produced by oxygen, typically occur around 100 km above the Earth’s surface.
- In contrast, the vibrant scarlet reds observed at higher altitudes (over 200 km) are a result of interactions between solar particles and oxygen at these elevations, indicating a higher energy level.
How do these particles originate from the Sun?
The Sun, a colossal sphere primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, undergoes various processes, including the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium, which generates charged particles like electrons. This massive ball of hot plasma possesses its own magnetic field, generated by internal convective currents. As it rotates, its surface experiences differential speeds, particularly at the equator compared to the poles, leading to complex magnetic loops that manifest as sunspots.
These charged particles, propelled by fusion and escaping from the Sun’s magnetic loops, travel vast distances and interact with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in the formation of aurorae at the poles—a true marvel of nature.
During geomagnetic storms, which can last from several hours to days, the auroral oval that encircles Earth’s poles can expand, providing even more opportunities to witness this phenomenon.
Do other planets experience aurorae?
Yes, any planet with a magnetic field and an atmosphere is likely to exhibit auroral activity. Astronomers have captured stunning images of aurorae on planets such as Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
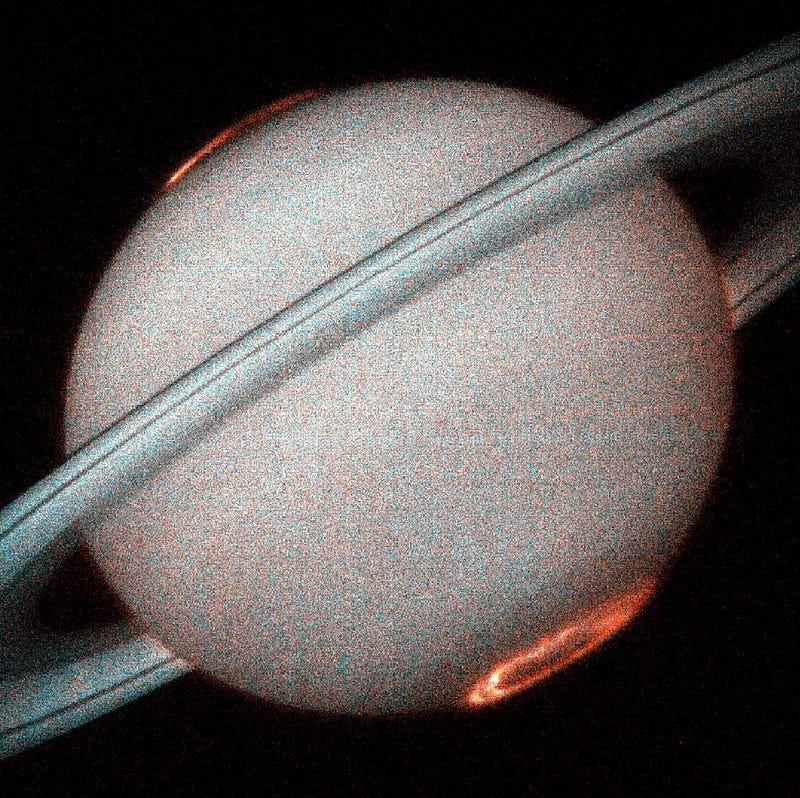
Image Credit: NASA — Saturn
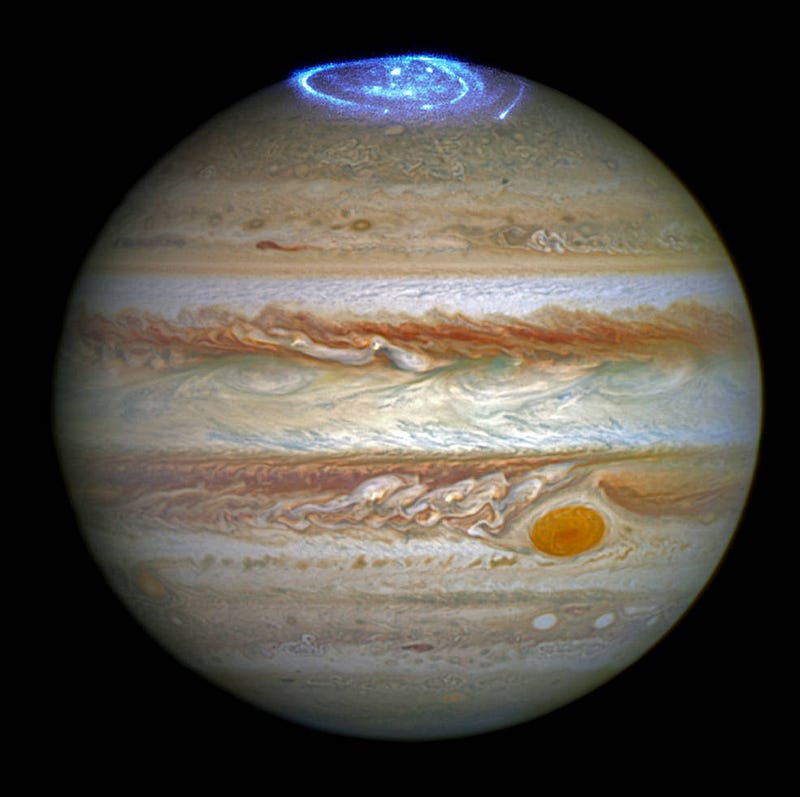

Credits: NASA, ESA, and J. Nichols (University of Leicester) — Jupiter
It's worth noting that the auroras observed on Saturn and Jupiter are primarily ultraviolet in nature, making them invisible to the naked eye as they fall outside the visible light spectrum.
Next time you find yourself gazing at the aurorae, remember the scientific principles that underpin their beauty. You might even feel inspired to delve deeper into the physics of these extraordinary phenomena and appreciate the wonders of the universe we inhabit.
I hope you found this article enlightening and that you gained insights you weren’t previously aware of. Have a wonderful day!
In this video, "The Science Behind the Northern Lights," we delve into the intriguing physics and processes that create these stunning natural displays.
This video, "Northern Lights Physics Explained in 6 Minutes," provides a concise overview of the scientific explanations behind the auroras.