Understanding Data Lakes and Data Hubs: Key Differences Explained
Written on
Chapter 1: Overview of Data Storage Solutions
Data Lakes and Data Hubs, sometimes referred to collectively as Datahub, represent distinct types of data storage systems. A Data Lake typically retains unrefined data in its natural format, while a Data Hub features a central storage framework that disseminates data across various domains following a star architecture.
Definition of a Data Hub
A Data Hub acts as a seamless exchange platform, facilitating the effortless flow of data. It encompasses a range of technologies, including Data Warehousing, Engineering, and Data Science. Rather than merely a technological solution, it embodies a strategic methodology aimed at optimizing when, where, and for whom data should be processed, shared, and stored. Various endpoints—such as applications, algorithms, processes, and users—interact with the hub, often in real time, to either supply or retrieve data.
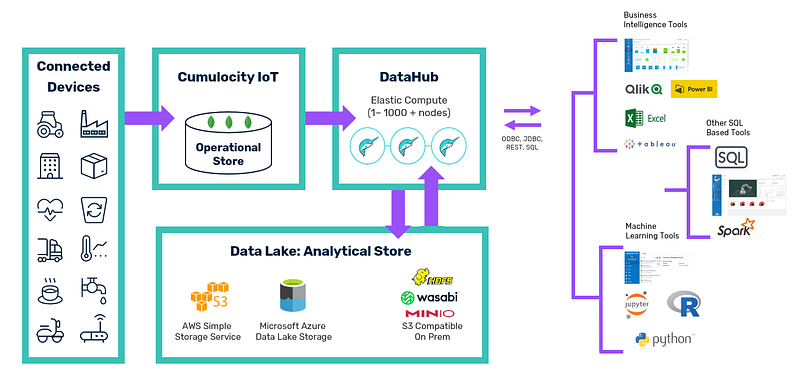
Data Hub in Practice
For instance, the Data Hub is implemented in Dremio, a distributed SQL engine that provides an SQL API accessible via JDBC, ODBC, and REST protocols. Dremio is responsible for the Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) processes, channeling data from Internet of Things (IoT) sources into a Data Lake and various analytical tools. For a more thorough exploration of this topic, feel free to click here.
Distinction from Data Warehouses and Lakes
While Data Warehouses and Data Lakes are typically viewed as endpoints for data accumulation to support organizational analytics, Data Hubs function as intermediaries for data exchange. Below is a summary comparing the characteristics of these three solutions.
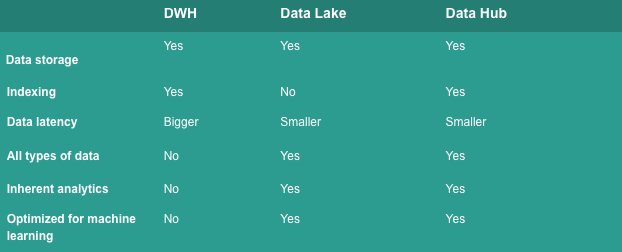
Data Lakes may also perform processing and relay data to a Data Warehouse (known as the Data Lakehouse approach), but they do not generally provide data accessibility across the organization. Moreover, the performance of a Data Lake may not be optimal since its primary role is data analysis. In contrast, a Data Hub is specifically engineered for facilitating data exchange.
Chapter 2: Summary and Conclusion
In summary, a Data Hub consolidates enterprise data from diverse sources and formats to derive actionable insights. It is less about the technology itself and more about the strategic framework or platform it represents. A Data Hub distributes data within an organization, serving Data Lakes or Data Warehouses, which are often seen as long-term data repositories for storage and analysis. While both technologies serve different roles, they can be effectively integrated for varied applications.
The first video, "Data Hubs, Data Lakes, Data Warehouses: How are they different?" provides a comprehensive overview of how these systems compare and contrast in data management.
The second video, "Connecting the Dots with DataHub: Lakehouse and Beyond," dives deeper into the functionalities of Data Hubs and their relationship with Lakehouses.
Sources and Further Readings
[1] Computerweekly, Data Hub versus Data Lake: Wie unterscheiden sie sich? (2021)
[2] Eckerson, Data Hubs — What’s Next in Data Architecture? (2019)
[3] Cumulocity, DataHub overview (2022)